6. Editor Window¶
The Editor window of LAMMPS-GUI has most of the usual functionality that similar programs have: text selection via mouse or with cursor moves while holding the Shift key, Cut (Ctrl-X), Copy (Ctrl-C), Paste (Ctrl-V), Undo (Ctrl-Z), Redo (Ctrl-Shift-Z), Select All (Ctrl-A). When trying to exit the editor with a modified buffer, a dialog will pop up asking whether to cancel the exit operation, or to save or not save the buffer contents to a file.
The editor has an auto-save mode that can be enabled or disabled in the Preferences dialog. In auto-save mode, the editor buffer is automatically saved before running LAMMPS or before exiting LAMMPS-GUI.
6.1. Context Specific Word Completion¶
By default, LAMMPS-GUI displays a small pop-up frame with possible choices for LAMMPS input script commands or styles after 2 characters of a word have been typed.
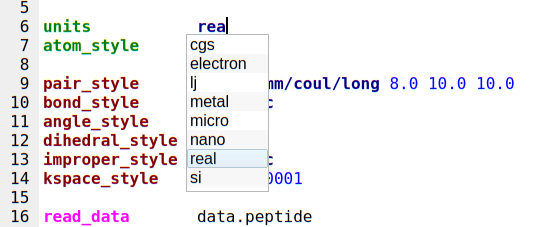
The word can then be completed through selecting an entry by scrolling up and down with the cursor keys and selecting with the ‘Enter’ key or by clicking on the entry with the mouse. The automatic completion pop-up can be disabled in the Preferences dialog, but the completion can still be requested manually by either hitting the ‘Shift-TAB’ key or by right-clicking with the mouse and selecting the option from the context menu. Most of the completion information is retrieved from the active LAMMPS instance and thus it shows only available options that have been enabled when compiling LAMMPS. That list, however, excludes accelerated styles and commands; for improved clarity, only the non-suffix version of styles are shown.
6.2. Line Reformatting¶
The editor supports reformatting lines according to the syntax in order to have consistently aligned lines. This primarily means adding whitespace padding to commands, type specifiers, IDs and names. This reformatting is performed manually by hitting the ‘Tab’ key. It is also possible to have this done automatically when hitting the ‘Enter’ key to start a new line. This feature can be turned on or off in the Preferences dialog for Editor Settings with the “Reformat with ‘Enter’” checkbox. The amount of padding for multiple categories can be adjusted in the same dialog.
Internally this functionality is achieved by splitting the line into “words” and then putting it back together with padding added where the context can be detected; otherwise a single space is used between words.
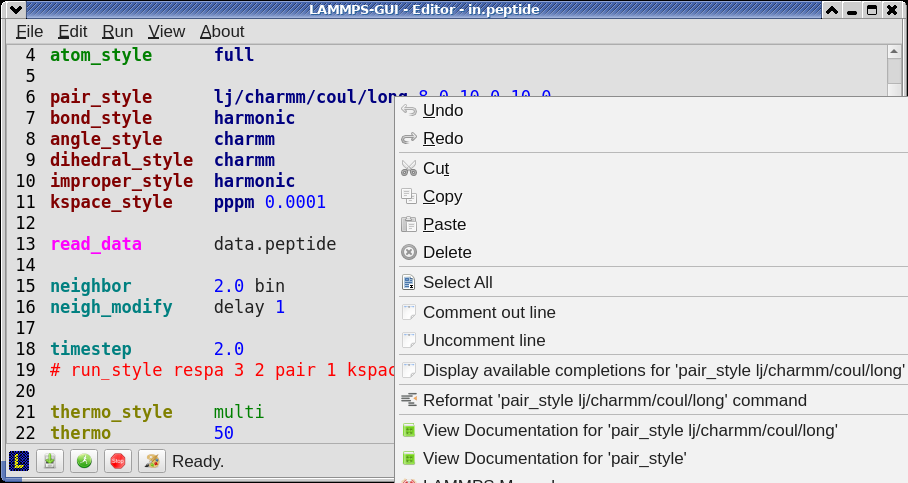
6.3. Context Specific Help¶
A unique feature of LAMMPS-GUI is the option to look up the LAMMPS documentation for the command in the current line. This can be done by either clicking the right mouse button or by using the Ctrl-? keyboard shortcut. When using the mouse, there are additional entries in the context menu that open the corresponding documentation page in the online LAMMPS documentation in a web browser window. When using the keyboard, the first of those entries is chosen.
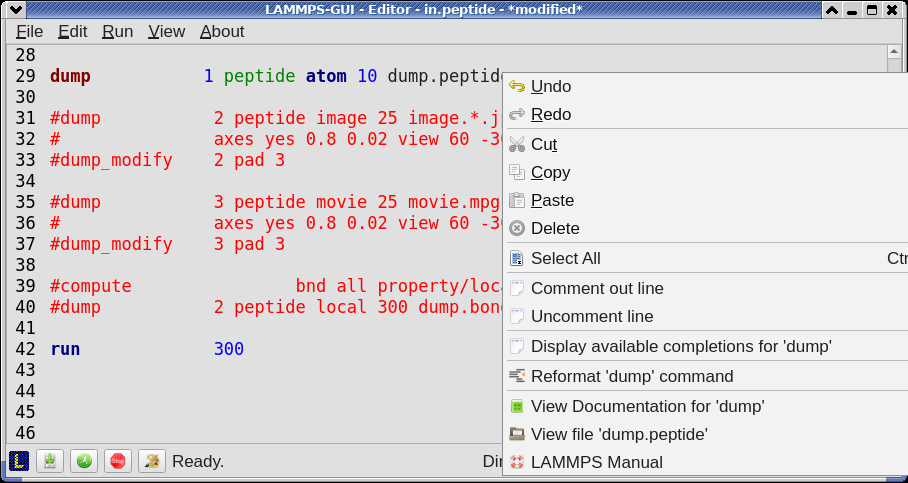
If the word under the cursor is a file, then additionally the context menu has an entry to open the file in a read-only text viewer window. If the file is a LAMMPS restart file, instead the menu entry offers to inspect the restart.
The text viewer is a convenient way to view the contents of files that are referenced in the input. The file viewer also supports on-the-fly decompression based on the file name suffix in a similar fashion as available with LAMMPS. If the necessary decompression program is missing or the file cannot be decompressed, the viewer window will contain a corresponding message.
6.4. Inspecting a Restart file¶
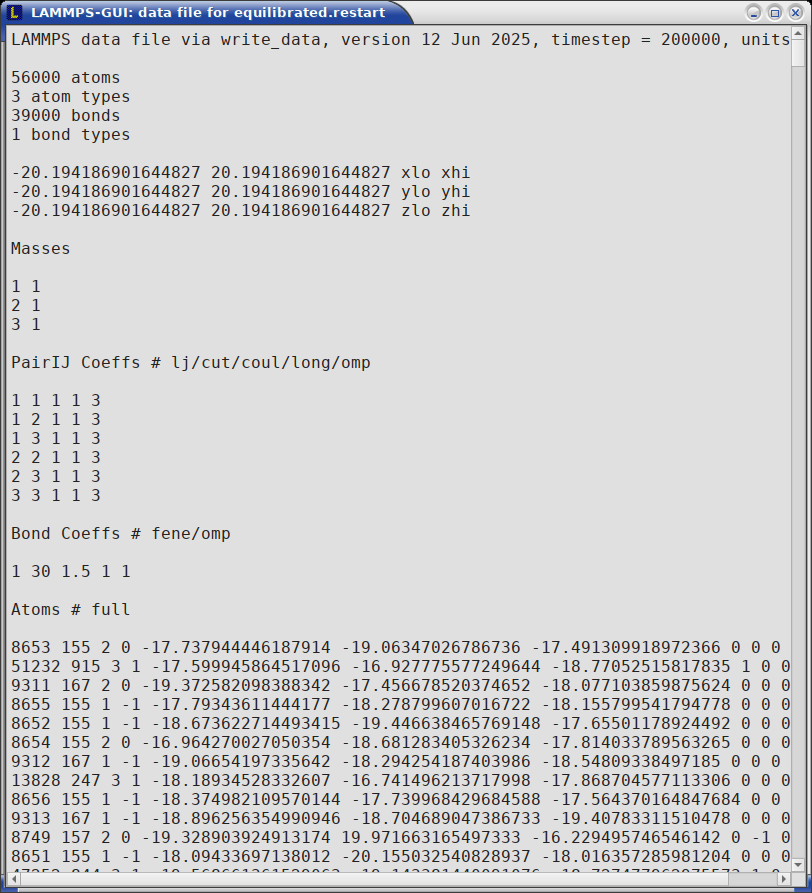
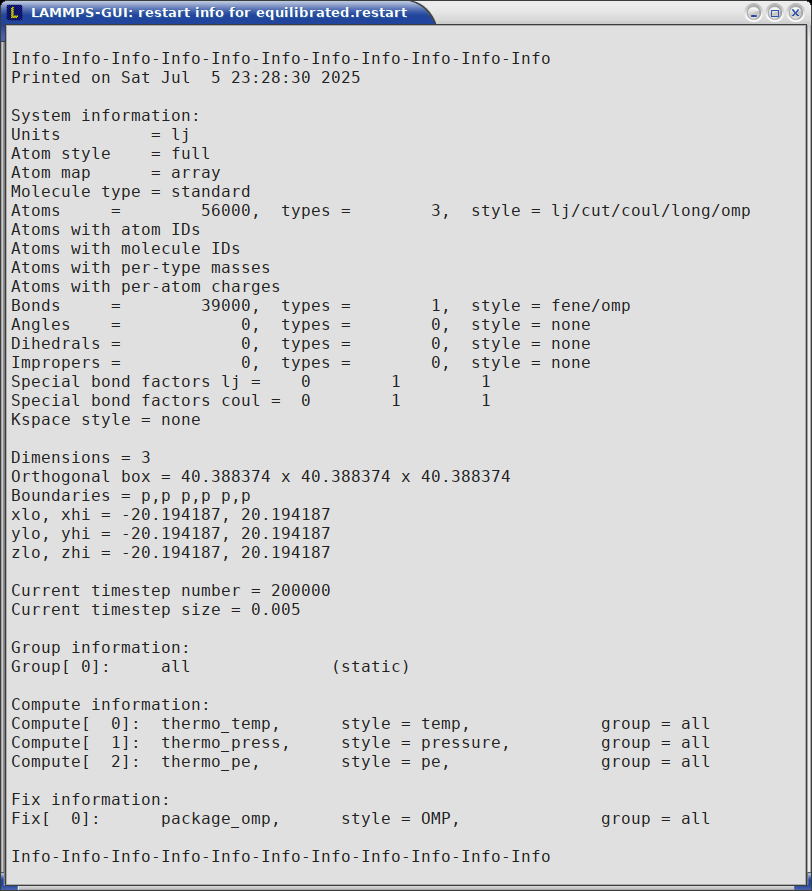
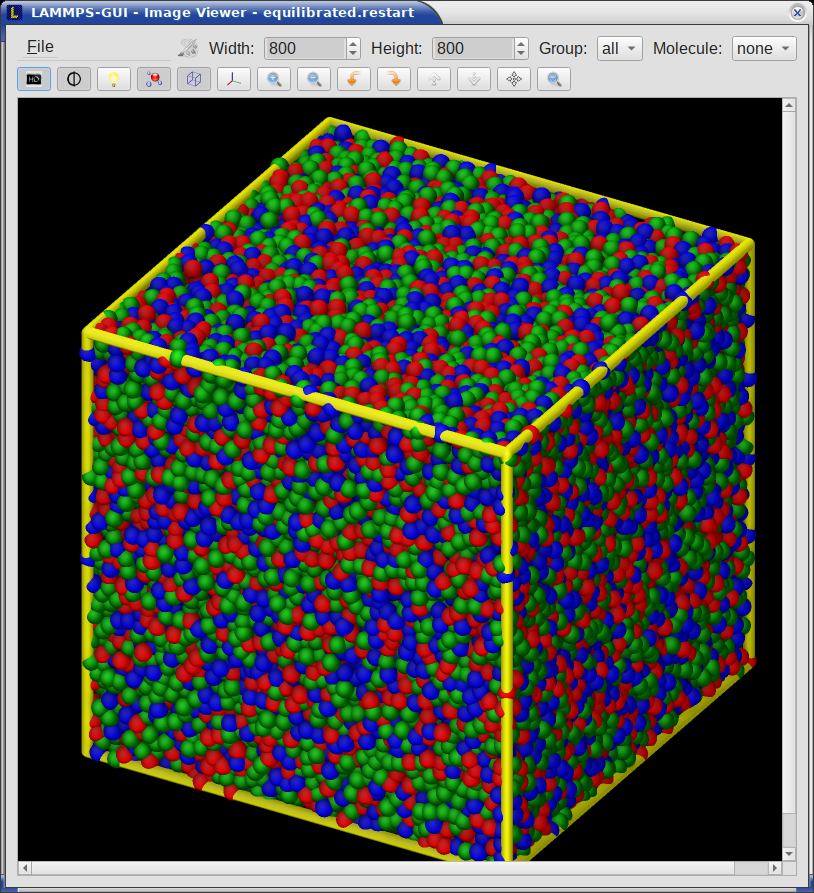
When LAMMPS-GUI is asked to “Inspect a Restart”, it will read the restart file into a LAMMPS instance and then open three different windows. The first window is a text viewer with the output of an info command with system information stored in the restart. The second window is text viewer containing a data file generated with a write_data command. The third window is a Snapshot Image Viewer containing a visualization of the system in the restart.
Large Restart Files
If the restart file is larger than 250 MBytes, a dialog will ask for confirmation before continuing, since large restart files may require large amounts of RAM since the entire system must be read into RAM. Thus restart file for large simulations that have been run on an HPC cluster may overload a laptop or local workstation. The Show Details… button will display a rough estimate of the additional memory required.